Vabljeno predavanje: dr. Michael E. Stuckelberger
Datum objave: 11.9.2024 Datum začetka: 18.9.2024 Ura začetka: 10:15 Lokacija: Multimedijska dvoranaV sredo, 18. septembra, bo na Fakulteti za elektrotehniko Univerze v Ljubljani potekalo vabljeno predavanje z naslovom “Mapping nanoscale performance in solar cells with X-rays”, ki ga bo izvedel dr. Michael E. Stuckelberger.
Dr. Michael E. Stuckelberger je vodja skupine za rentgensko nanoznanost in rentgensko optiko v nacionalnem raziskovalnem centru za temeljno znanost (DESY – Deutsches Elektronen-Synchrotron).
Povzetek predavanja v angleščini
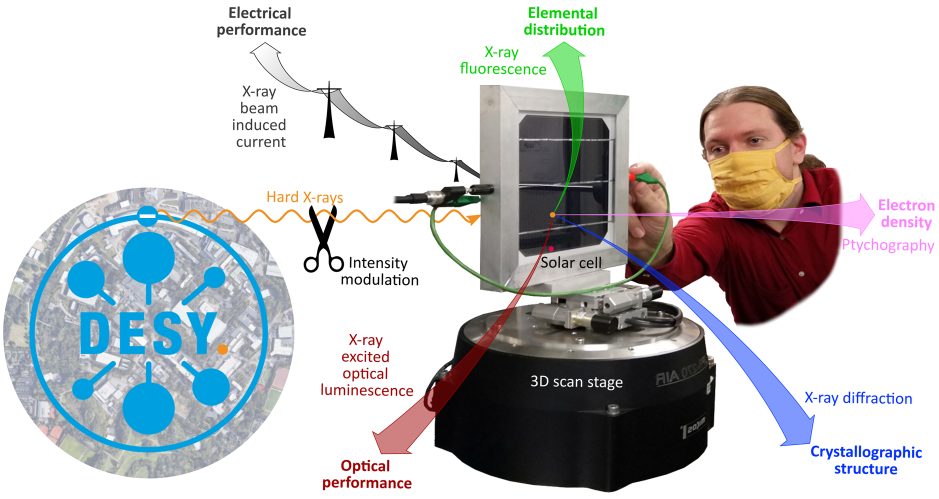
Scanning X-ray microscopy is ideally suited to tackle scientific and technological problems related to energy materials in general and to thin-film solar cells in particular. The problems may include:
- How does the charge collection efficiency vary in solar cells, and how does the distribution affect the overall device performance?
- Which roles play (trace) elements such as As or Se in CdTe, Rb in (Ag,Cu)(In,Ga)Se2, and Cs in metal-halide perovskites as dopant, defect, or defect passivator?
- How are crystallographic phases distributed in 3D, and how are they linked to nanoscale performance?
- How does nanoscale strain evolve during material growth, and how can it be engineered for desired properties?
In the presentation, we will (partially) answer these questions and showcase scanning X-ray microscopy examples from leading nano- and microprobe beamlines in Europe and the US. Yet, many questions remain without answer and challenge the characterization community at several levels. In view of ever brighter nanoprobes at diffraction-limited storage rings offering access to users, we give an outlook to ongoing technological and methodological developments that include:
- Assessment of the temporal and spectral response of semiconductor materials and solar cells through temporally resolved (TR-XEOL) and spectrally resolved X-ray excited optical luminescence (SR-XEOL)
- Assessment of the nanoscale performance of solar cells through X-ray beam induced current (XBIC)
Maybe this presentation can trigger future collaborations? Our instruments are accessible to general users.